1- Definition of Megatrend
According to Frost and Sullivan, a megatrend is a large, social, economic, political, environmental or technological change that is slow to form. Once in place, megatrends influence a wide range of activities, processes and perceptions, both in government and in society, possibly for decades. They are the underlying forces that drive trends. (i.e. aging population)
A trend is an emerging pattern of change likely to impact state government and require a response. (i.e. adult children taking care of parents)
• Does it impact the states?
• Is it significant? Is it broad-based? Is it national or regional in scope?
• Is it short-term or long-term?
• Is it measurable/ trackable/ observable?
• Is it actionable? Is there an innovative response to address new circumstances?
In the other way, Mega Trends are global, sustained and macroeconomic forces of development that impact business, economy, society, cultures and personal lives, thereby defining our future world and its increasing pace of change.
These Mega Trends set the stage for visionary thinking by identifying the most important global macro forces, potential scenarios of specific trends in 2020, and the implications of these Mega Trends in transforming society, markets and cultures.
A trend is an emerging pattern of change likely to impact state government and require a response. (i.e. adult children taking care of parents)
• Does it impact the states?
• Is it significant? Is it broad-based? Is it national or regional in scope?
• Is it short-term or long-term?
• Is it measurable/ trackable/ observable?
• Is it actionable? Is there an innovative response to address new circumstances?
In the other way, Mega Trends are global, sustained and macroeconomic forces of development that impact business, economy, society, cultures and personal lives, thereby defining our future world and its increasing pace of change.
These Mega Trends set the stage for visionary thinking by identifying the most important global macro forces, potential scenarios of specific trends in 2020, and the implications of these Mega Trends in transforming society, markets and cultures.
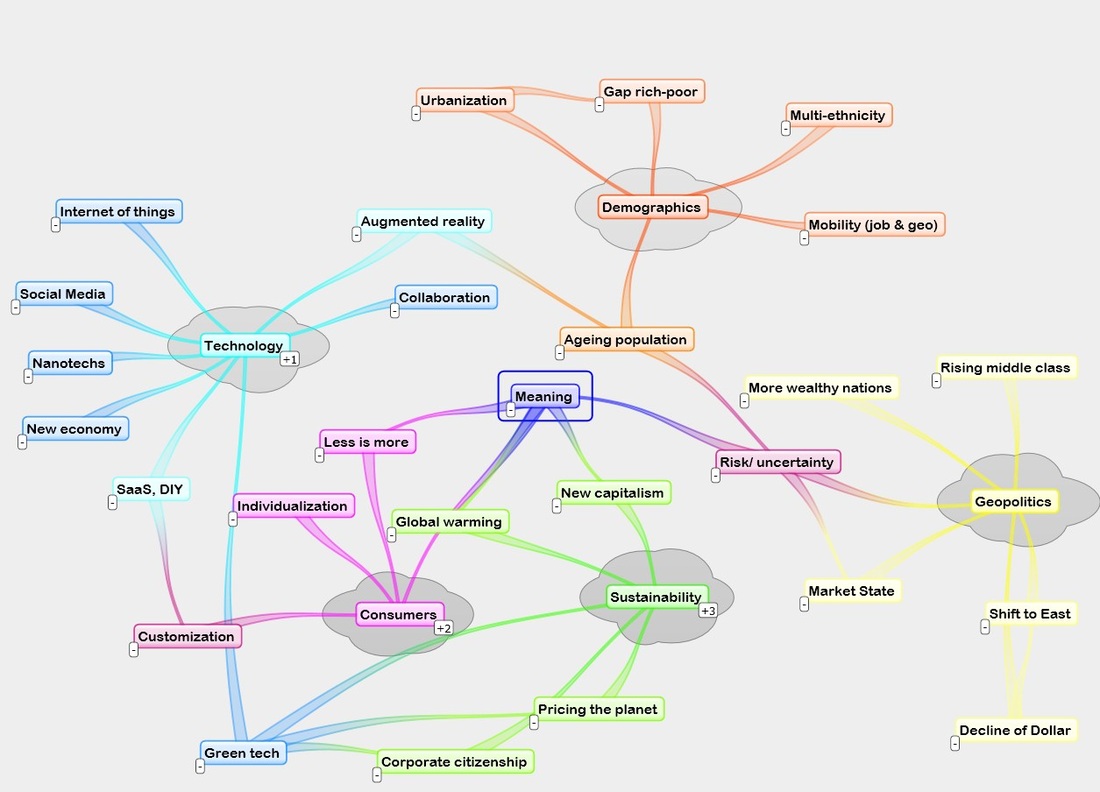
2- Categories of Megatrends
Category 1: Demographic Shifts
Demographic shifts refer to changes in various aspects of population statistics, such as size, racial and ethnic makeup, birth and mortality rates, geographic distribution, age and income.
Megatrend: Aging population
Trends: buying habits, elder care, health care, workforce gaps when baby boomers retire
Megatrend: Immigration/diversity
Trends: government service provision, capacity to fill gaps in workforce
Megatrend: Population growth
Trends: demands and effects on land, climate, water, government resources, schools
Megatrend: Suburbanization/sprawl
Trends: demands and effects on land, climate, water supply, small business, entrepreneurship, government resources
Demographic shifts refer to changes in various aspects of population statistics, such as size, racial and ethnic makeup, birth and mortality rates, geographic distribution, age and income.
Megatrend: Aging population
Trends: buying habits, elder care, health care, workforce gaps when baby boomers retire
Megatrend: Immigration/diversity
Trends: government service provision, capacity to fill gaps in workforce
Megatrend: Population growth
Trends: demands and effects on land, climate, water, government resources, schools
Megatrend: Suburbanization/sprawl
Trends: demands and effects on land, climate, water supply, small business, entrepreneurship, government resources
Category 2: Changes in Political Conditions
Changes in political conditions refer to dynamics related to the process of electing officials as well as process of formulating and implementing public policy and programs.
Megatrend: Election issues
Trends: campaign finance reform, redistricting, term limits
Megatrend: Federalism
Trends: distribution of authority from one presidency and Congress to another, impact of federal policies on state governments (including international trade agreements)
Megatrend: Participatory democracy
Trends: voting systems (including e-voting), lobbying, initiatives, referendums
Megatrend: Privatization/outsourcing
Trends: private companies providing public services, sending jobs overseas
Changes in political conditions refer to dynamics related to the process of electing officials as well as process of formulating and implementing public policy and programs.
Megatrend: Election issues
Trends: campaign finance reform, redistricting, term limits
Megatrend: Federalism
Trends: distribution of authority from one presidency and Congress to another, impact of federal policies on state governments (including international trade agreements)
Megatrend: Participatory democracy
Trends: voting systems (including e-voting), lobbying, initiatives, referendums
Megatrend: Privatization/outsourcing
Trends: private companies providing public services, sending jobs overseas
Category 3: Science and Technology Developments
Science and technology developments are advancements in both scientific research and applications of that research.
Megatrend: Bioengineering
Trends: DNA, stem cell research, cloning, genetic engineering
Megatrend: Energy sources
Trends: development of alternative energy sources
Megatrend: Privacy and security issues
Trends: wireless tracking, identity theft, cyber terrorism
Megatrend: Electronic delivery of goods/services
Trends: e-commerce, e-government
Science and technology developments are advancements in both scientific research and applications of that research.
Megatrend: Bioengineering
Trends: DNA, stem cell research, cloning, genetic engineering
Megatrend: Energy sources
Trends: development of alternative energy sources
Megatrend: Privacy and security issues
Trends: wireless tracking, identity theft, cyber terrorism
Megatrend: Electronic delivery of goods/services
Trends: e-commerce, e-government
Category 4: Economic Dynamics
Economic dynamics are changes in the production and exchange of goods and services both within and between nations as well as movements in the overall economy such as prices, output, unemployment, banking, capital and wealth.
Megatrend: Globalization of trade
Trends: outsourcing, offshoring, free trade agreements, prescription drug reimportation
Megatrend: Energy supply
Trends: price increases, availability
Megatrend: Intellectual property
Trends: standardization of local, state, national and international regulations
Megatrend: Retirement issues
Trends: move away from defined benefit plans, pension shortfall, Social Security
Economic dynamics are changes in the production and exchange of goods and services both within and between nations as well as movements in the overall economy such as prices, output, unemployment, banking, capital and wealth.
Megatrend: Globalization of trade
Trends: outsourcing, offshoring, free trade agreements, prescription drug reimportation
Megatrend: Energy supply
Trends: price increases, availability
Megatrend: Intellectual property
Trends: standardization of local, state, national and international regulations
Megatrend: Retirement issues
Trends: move away from defined benefit plans, pension shortfall, Social Security
Category 5: Social and Cultural Shifts
Social and cultural shifts are changes in core values, beliefs, ethics and moral standards that direct peoples’ behavior and can influence their participation in the formulation of public policy.
Megatrend: Government involvement in social policy
Trends: gay marriage, abortion, separation of church and state issues
Megatrend: Redefinition of family and role of family
Trends: single-headed households, unmarried couples, home schooling
Megatrend: Redefinition of morality
Trends: re-evaluating definition of indecency, censorship issues
Megatrend: Spirituality
Trends: homeopathic medicine, spiritual beliefs may be different than religious beliefs
Megatrend: Assimilation
Trends: shift from acculturation to maintaining ethnic identities
Social and cultural shifts are changes in core values, beliefs, ethics and moral standards that direct peoples’ behavior and can influence their participation in the formulation of public policy.
Megatrend: Government involvement in social policy
Trends: gay marriage, abortion, separation of church and state issues
Megatrend: Redefinition of family and role of family
Trends: single-headed households, unmarried couples, home schooling
Megatrend: Redefinition of morality
Trends: re-evaluating definition of indecency, censorship issues
Megatrend: Spirituality
Trends: homeopathic medicine, spiritual beliefs may be different than religious beliefs
Megatrend: Assimilation
Trends: shift from acculturation to maintaining ethnic identities